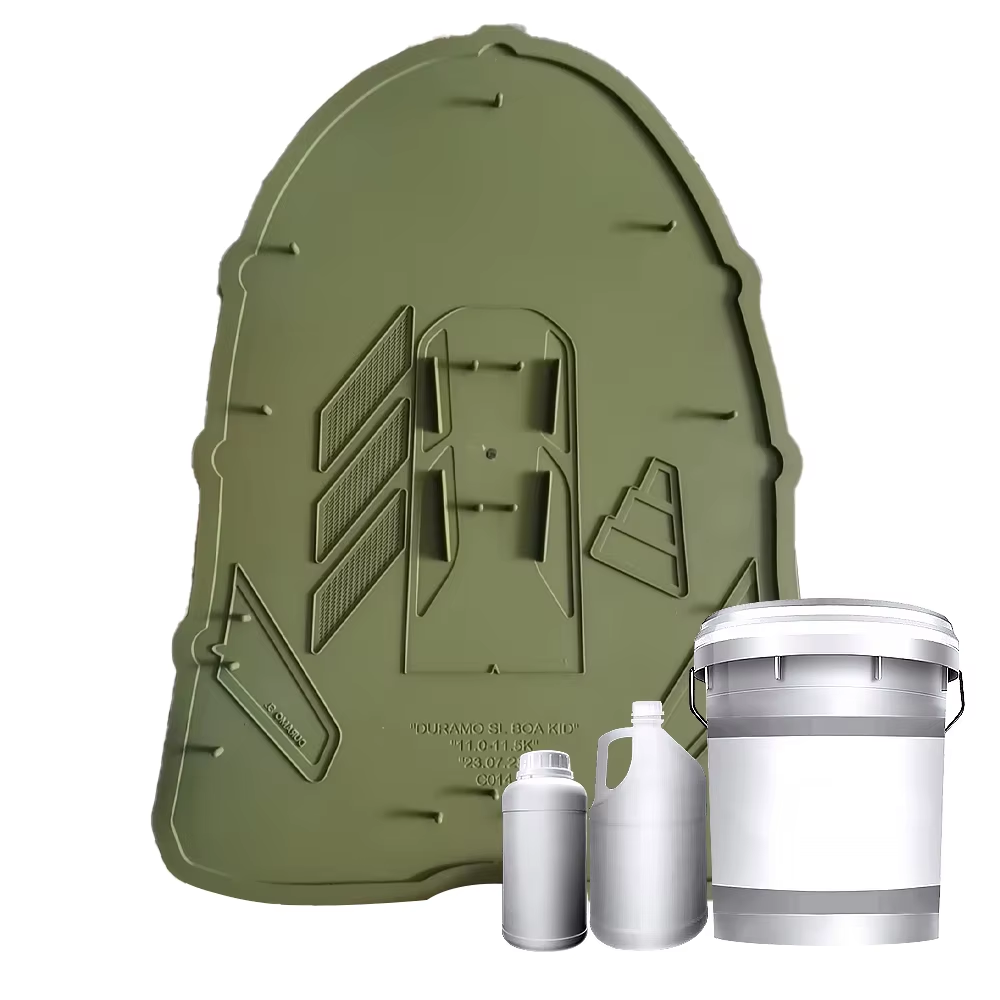
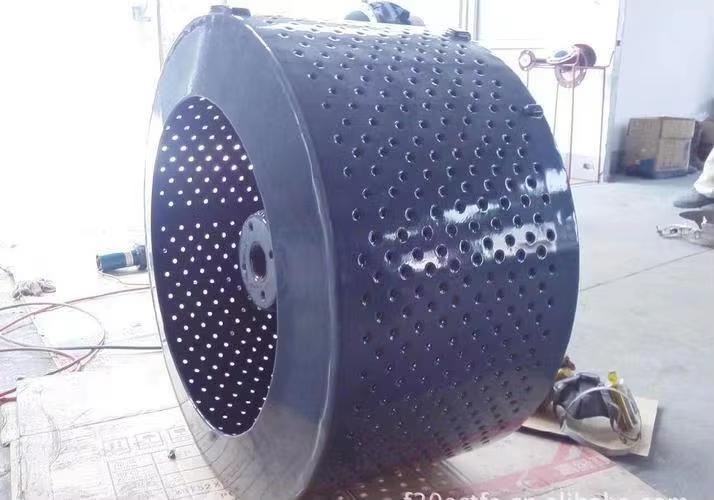
PTFE non stick coating thickness is a critical parameter that directly influences the performance, durability, and functionality of the coating across various applications, from kitchenware to industrial machinery. The optimal PTFE non stick coating thickness typically ranges from 25 to 75 microns, though this can vary based on the specific use case—thinner coatings (25-50 microns) are ideal for applications requiring flexibility, such as on rubber molds or small precision parts, where a thick layer might impede movement or conformability, while thicker coatings (50-75 microns) are preferred for high-wear industrial settings, like machinery components or chemical processing equipment, where enhanced durability is needed. PTFE non stick coating thickness must be carefully controlled during application to ensure uniformity, as uneven thickness can lead to inconsistent non-stick performance, with thinner areas prone to premature wear and thicker areas at risk of cracking under thermal stress. In kitchenware, PTFE non stick coating thickness is balanced to provide sufficient non-stick properties without compromising heat transfer, ensuring even cooking while resisting scratches from metal utensils. For industrial molds used in rubber or silicone production, PTFE non stick coating thickness is optimized to facilitate easy release of parts without adding excessive bulk that could alter mold dimensions. The application process, whether spray or dip coating, is calibrated to achieve the desired PTFE non stick coating thickness, with quality control measures like micrometer checks to verify consistency. Proper PTFE non stick coating thickness also enhances chemical resistance, as a uniform layer ensures complete coverage, protecting the substrate from corrosive substances in chemical industry applications. Ultimately, PTFE non stick coating thickness is a key factor in balancing performance, durability, and cost, making it a critical consideration in coating selection and application.